Levator scapulae
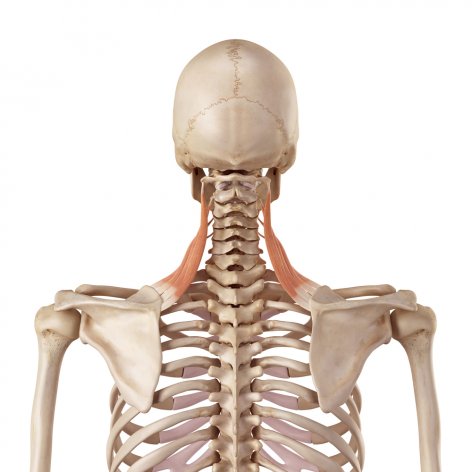
- Fiber direction: Extends vertically from the transverse processes of C1–C4, then twists at the midpoint and attaches to the superior portion of the medial border of the scapula
- Nerve innervation: Dorsal scapular nerve C3, C4, C5
- Has a distinctive twist in the fibers in the middle of the muscle
- Synergistic with the trapezius and rhomboid muscles
- Stiffness in the neck is often caused by overuse of the levator scapulae, common with carrying heavy bags on one shoulder, excessive lifting, or unconscious shoulder elevation in response to stress.
Origin:
Transverse processes of C1–C4
Insertion:
Medial border of the scapula, from the superior angle to the root of the spine of the scapulaAction: Elevates the scapula at the scapulothoracic joint
Selected Synergists: Trapezius (upper), Rhomboid major, Rhomboid minor
Selected Antagonists: Serratus anterior, Pectoralis minor, Trapezius (lower)
Action: Downwardly rotates the scapula at the scapulothoracic joint
Selected Synergists: Rhomboid major, Rhomboid minor, Pectoralis minor
Selected Antagonists: Trapezius (upper and lower), Serratus anterior
Action: Unilaterally: Laterally flexes the head and neck to the same side (ipsilaterally)
Selected Synergists: Same side: Trapezius (upper), Sternocleidomastoid, Scalenes, Splenius capitis, Splenius cervicis, Longus capitis, Longus colli
Selected Antagonists: Opposite side: Trapezius (upper), Sternocleidomastoid, Scalenes, Splenius capitis, Splenius cervicis, Longus capitis, Longus colli
Action: Unilaterally: Rotates the head and neck to the same side (ipsilaterally)
Selected Synergists: Same side: Splenius capitis, Splenius cervicis
Selected Antagonists: Opposite side: Splenius capitis, Splenius cervicis
Action: Bilaterally: Extends the head and neck
Selected Synergists: Bilaterally: Trapezius (upper), Splenius capitis, Splenius cervicis
Selected Antagonists: Bilaterally: Sternocleidomastoid, Scalene (anterior), Longus capitis, Longus colli
- Article: Christy Cael, “Levator Scapulae,” Massage & Bodywork (May/June 2009): 97–98, www.massageandbodyworkdigital.com/i/68013-may-june-2009/97.
- Article: Joseph E. Muscolino, “Integrating Science with Technique,” Massage & Bodywork (March/April 2016): 60–71, www.massageandbodyworkdigital.com/i/640605-march-april-2016/62.
- Article: Til Luchau, “Shoulder/Neck Differentiation,” Massage & Bodywork (March/April 2016): 108–109, www.massageandbodyworkdigital.com/i/640605-march-april-2016/110.
- Webinar: Douglas Nelson, “Precision Neuromuscular Therapy 3: Upper Extremity,” available at www.abmp.com/members/continuing-education/online-learning/courses/webina....
- Webinar: Douglas Nelson, “Assessment and Methods for the Shoulder Girdle,” available at www.abmp.com/members/continuing-education/online-learning/courses/webina....
- Webinar: Joseph E. Muscolino, DC, “Learn to Palpate Effectively,” available at www.abmp.com/members/continuing-education/online-learning/courses/webina....

